Definition of Rotational Slip in Geography
What is Mass Movement?
Mass Movement is the downhill movement of cliff material under the influence of gravity. There is a range of different types of mass movement. These are explored below.
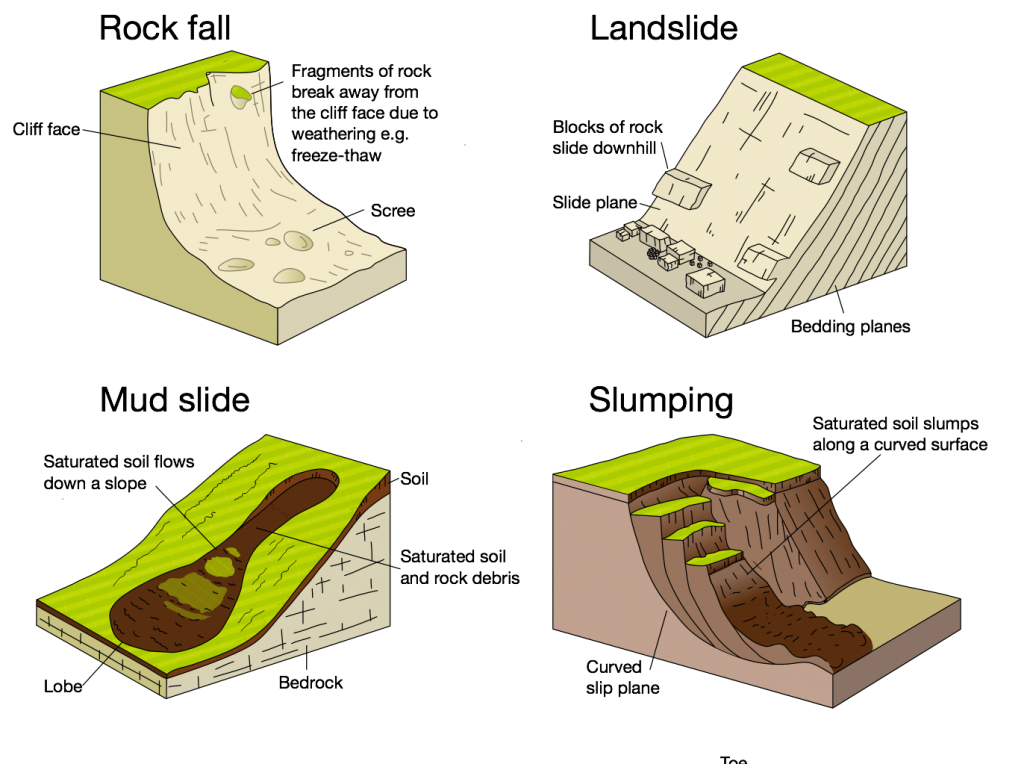
Types of mass movement
Slumping / Rotational Slip
Cliffs formed from boulder clay, material deposited by glacial periods, are susceptible to high rates of coastal erosion. The Holderness Coast is an example of a coastline formed from boulder clay and is the fastest eroding coastline in Europe. The soft boulder clay is quickly eroded through hydraulic action and abrasion. However, this is not the only way it is being eroded. Sub-aerial processes, such as rainfall, also cause erosion. This often happens where layers of boulder clay, left behind by melting glaciers, become saturated and cause the cliff to slump. The debris on the beach is then eroded by the sea leaving the cliff exposed once more.
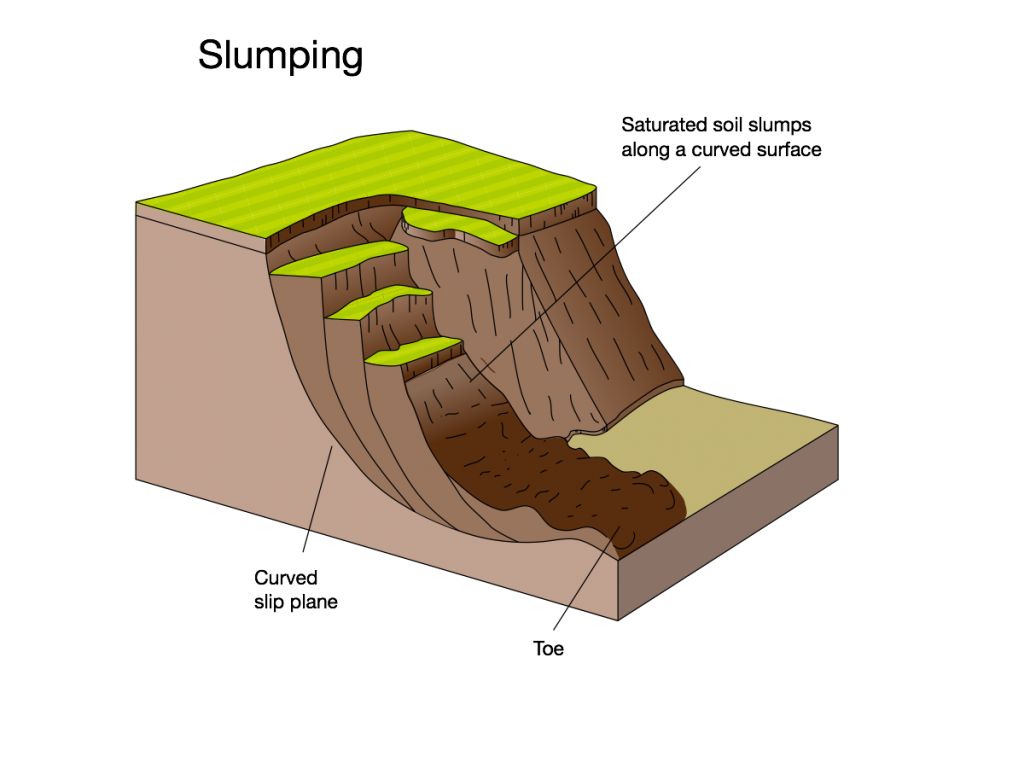
An annotated diagram showing the main features of slumping.
Slumping explained:
Stage 1 – the soft boulder clay holds rainwater and run-off.
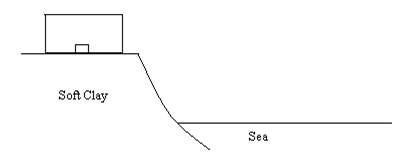
Slumping stage 1
Stage 2 – Waves erode the base of the cliff creating a wave-cut notch. The clay becomes saturated and forms a slip plane.
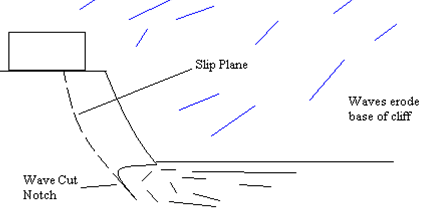
Slumping stage 2
Stage 3 – The weight of the saturated cliff causes it to slump.
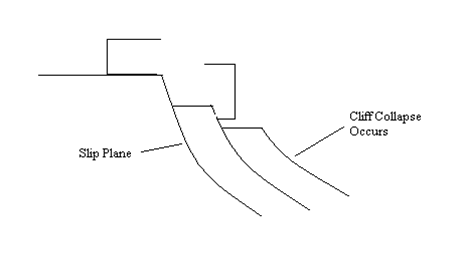
Slumping stage 3
The video below shows evidence of slumping at Mappleton, Holderness Coast. The video shows the early stages of the process. Water will percolate down the large crack to lubricate the slip plane. This will cause the land to slump further down.
Landslides
In areas of more resistant cliff material erosion is greatest when waves break at the foot of a cliff. This causes erosion at the base of the cliff. This creates a wave-cut notch in the base of the cliff. As the notch increases in size, the weight of the cliffs above become too much to support which leads to a landslide. This material will provide temporary protection for the cliff behind. However, once it has been removed by the sea this process will occur again. Where cliffs are made of more resistant material, wave-cut platforms will be created.
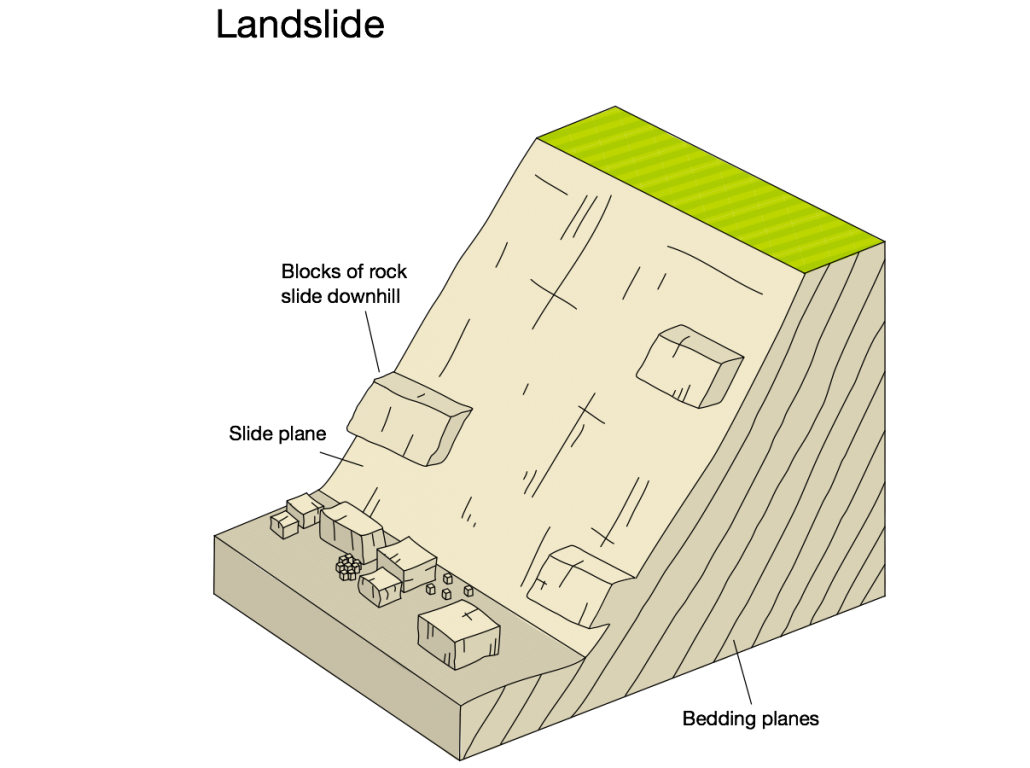
An annotated diagram showing the main features of a landslide.
The image below shows a landslide at West Bay, Dorset.
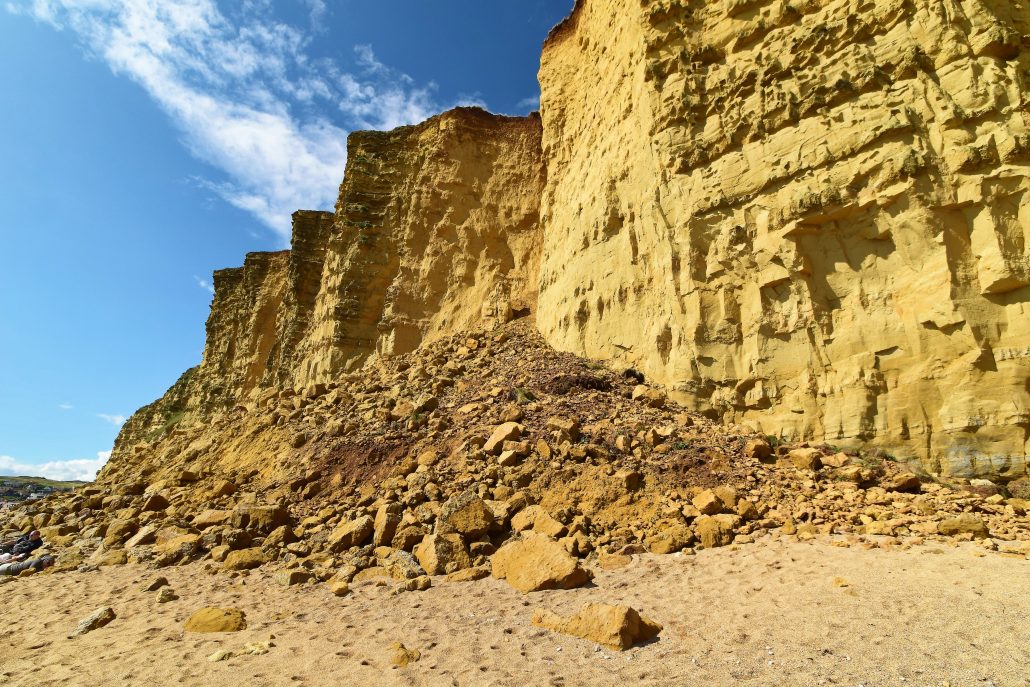

Landslide at West Bay on Dorset's Jurassic Coast.
The video below shows evidence of a landslide at Port Mulgrave, Yorkshire and Cleveland Heritage Coast.
Rockfall
A rockfall involves fragments of rock breaking away from the cliff face, often due to freeze-thaw weathering.
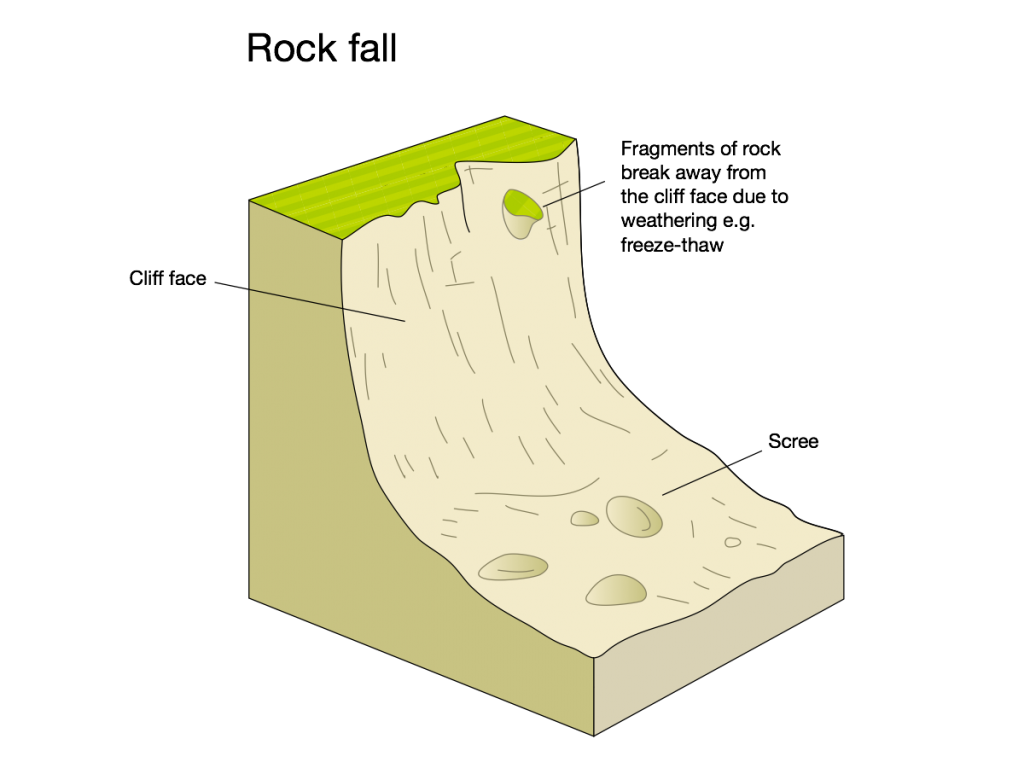
An annotated diagram showing the main features of a rock fall.
The video below shows a series of rock falls above a landslide at Port Mulgrave, Yorkshire.
Mudslide
Mudslides occur when saturated soil and weak rock flows down a slope. These typically occur where cliffs are made up of boulder clay.
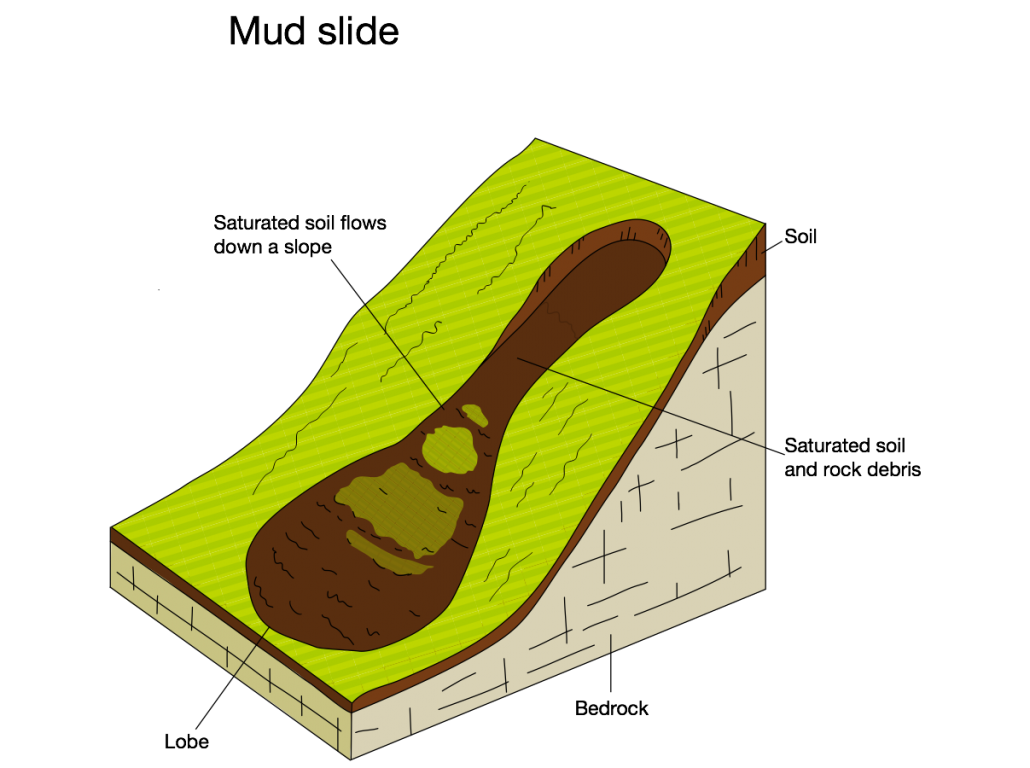
An annotated diagram showing the main features of a mudslide.
The image below shows a mudslide at Mappleton, Holderness Coast.
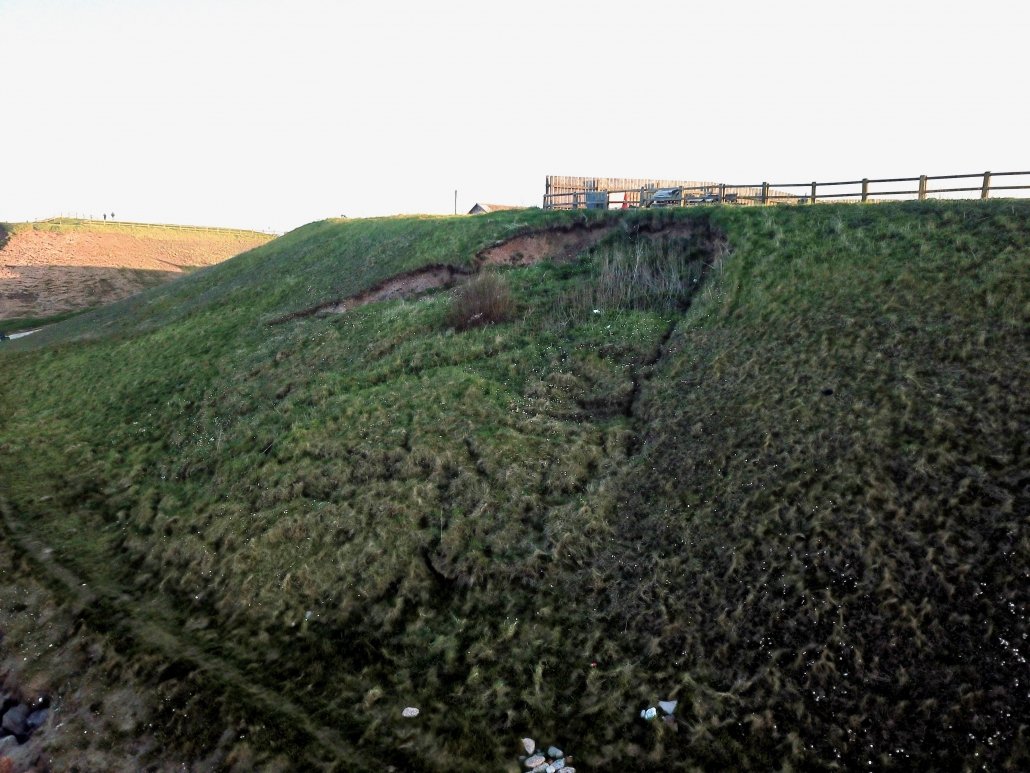

A mudslide at Mappleton
The video below shows evidence of a mudslide at Mappleton.
The video below shows evidence of a small mudflow at Hornsea, Holderness Coast.
You can view more videos on the mass movement video page.

Definition of Rotational Slip in Geography
Source: https://www.internetgeography.net/topics/what-is-mass-movement/
0 Response to "Definition of Rotational Slip in Geography"
Post a Comment